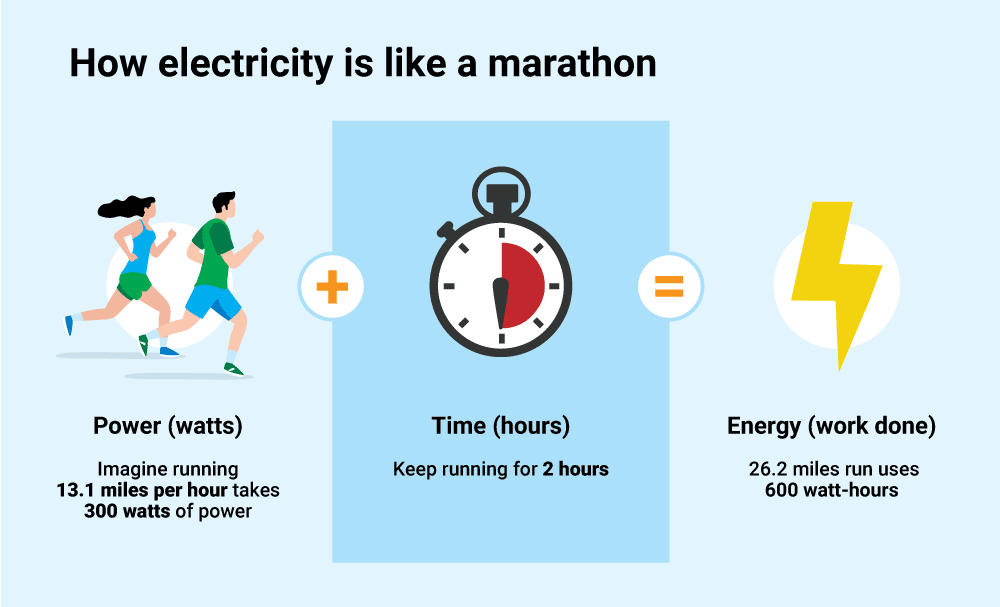
work done vs power
If a carton of books is moved from the. Power decides how quickly work could be done it is interlinked with work.

Solved How Does The Work Compare Walking Up The Stairs Vs Chegg Com
Power is the rate at which work is done.

. Work is independent of time. Force exerted on the body. If you do 100 joules of work in one second using 100 joules of energy the power is 100 watts.
Power is the rate of energy consumed in a unit of time Power Work time. And the object with energy can exert force on another object to transfer energy. Lesson 1 - Basic Terminology and Concepts.
Work describes the amount of energy. Power and work are two very important concepts discussed in mechanics. Power vs Work.
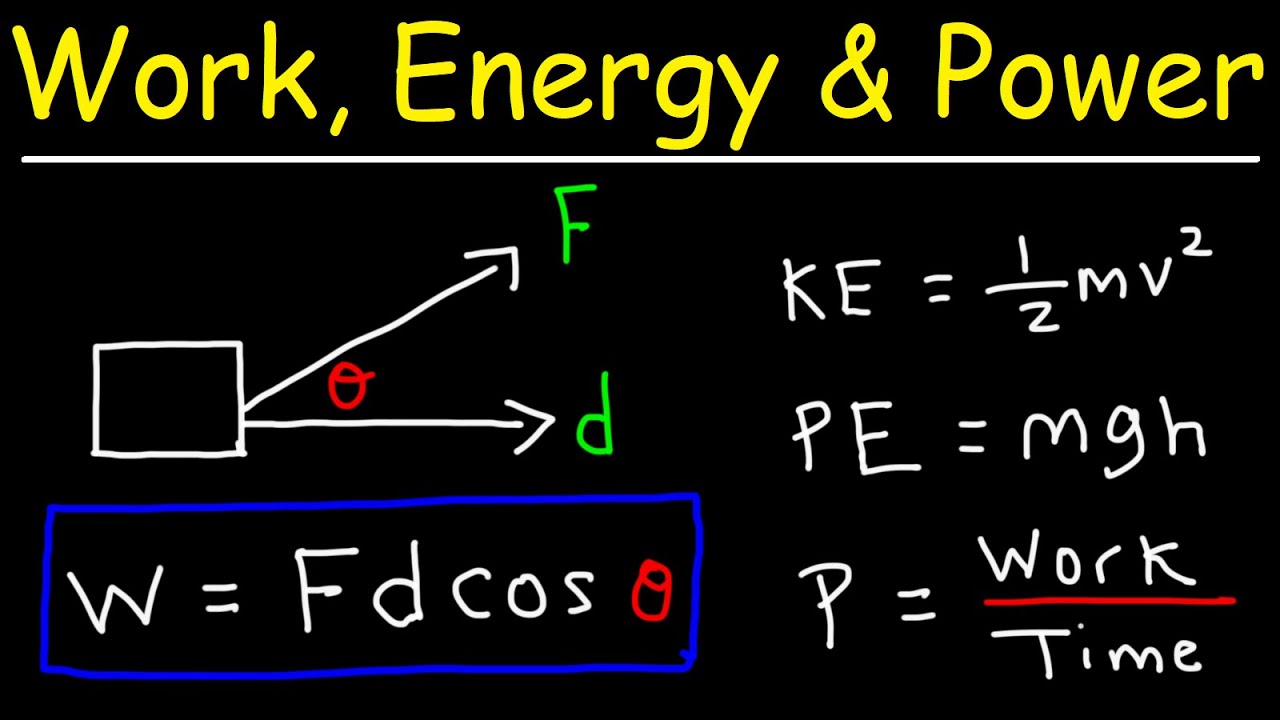
The work done by a force 100 N moving a body 50 m can be calculated as. Work is a scalar quantity. Power is a comparatively less used concept but is of the same importance.
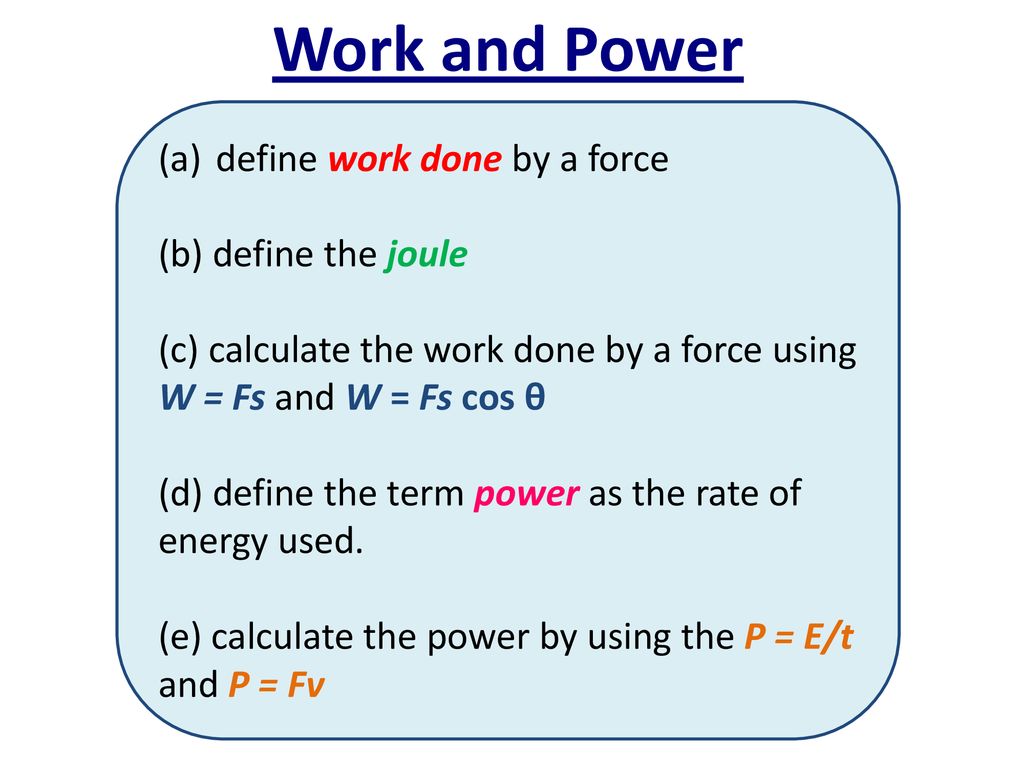
Power is the work done per unit of time. As is implied by. Mathematically it is computed using the following equation.
Example - Work done by a Force. Studying work energy power is important in terms of both acquiring knowledge and getting higher marks in the exam. Power describes the rate of energy transfer.
Difference between Work and Power. Work done is the same as energy transferred. In the case of work done object working loses energy while work done on an object gains energy.
In exercise its the rate of performing muscular work with potential energy. Power is a scalar quantity. Conservation of energy links GPE KE and work done.
Power is a time-dependent quantity. Power refers to the rate at which. Power is the rate of transfer of energy or the rate of doing work.
It is the worktime ratio. Calculating the Amount of Work Done by Forces. The standard metric unit of power is the Watt.
Work and Energy. But power is more used in regular life when compared to work. The SI unit of power is Watt W.
Is the rate of doing work or the rate of using energy which are numerically the same. Work is the most frequently used concept in our regular living. Definition and Mathematics of Work.
W 100 N 50 m 5000 Nm J The unit of work is joule J which is defined. Work is the total amount of energy that is used to shift an object from one place to another by applying an outside force for example. Work Force Displacement.
The factors that affect the work done by an object is. The SI unit of work is Joule J.

Work Energy Power Physical Work Work W Is Defined As The Force F Times The Distance S Moved In The Direction Of The Force Cos 8 Nb 8 Is Angle
Unit 4 Work And Energy Physics Project
Intro To Work And Power Regents Physics

Comparison Of Specific Work Output Or Power Output Per Unit Working Download High Quality Scientific Diagram

Electrical Energy Power And Charge
Definition And Mathematics Of Work
Work Vs Power Lab Teaching Resources Teachers Pay Teachers
Work Energy And Power Basic Introduction Youtube

Exam2notes 206 Describes How To Use Forces The Work Energy Theorem Momentum And The Studocu

Energy Work Power Work Done From The Force Vs Displacement Graph
Think Back To Gcse Define The Following Terms And See If You Can Make Any Connections Between Them Energy Work Power Time Distance Force Velocity Ppt Download

Work Done Power Definitions Formulas Concepts

P H Y S I C S Chapter 4 Work And Energy Section 4f Power Ppt Download

Work And Power Work Vs Impulse Similarities Both Have A Force Component Exerted On An Object Both Answer The Question How Long A Force Acts Differences Ppt Download